Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Disability
Thoracic outlet syndrome disability. Robinow syndrome is a rare disorder that affects the bones as well as other parts of the body. Neurogenic TOS from compression of the brachial plexus nerves venous TOS from compression of. Postural and overuse syndromes in students and office-based workers.
Patients complain about upper-limb paresthesia or weakness. Autosomal recessive Robinow syndrome and the milder autosomal dominant Robinow syndrome. The Medical Treatment Guidelines also called Medical Practice Guidelines or Review Criteria are evidence based and were developed by the Office of the Medical Director in.
Annals of Vascular Surgery provides solid peer reviewed coverage of clinical and experimental work in vascular surgery. Until the advent of electrophysiologic testing in the 1940s carpal tunnel syndrome CTS commonly was thought to be the result of compression of the brachial plexus by cervical ribs and other structures in the anterior neck region so-called thoracic outlet syndrome. Thoracic outlet syndrome This occurs when the collarbone shifts from its normal position and applies pressure to the blood vessels and nerves located between the bone and the highest rib.
Less common causes - Rib or compression fractures thoracic outlet syndrome and T4 syndrome. The medical treatment guidelines are written from a clinical perspective to guide clinical care. Most children with Robinow syndrome experience growth delays after birth resulting in slight to moderate short stature.
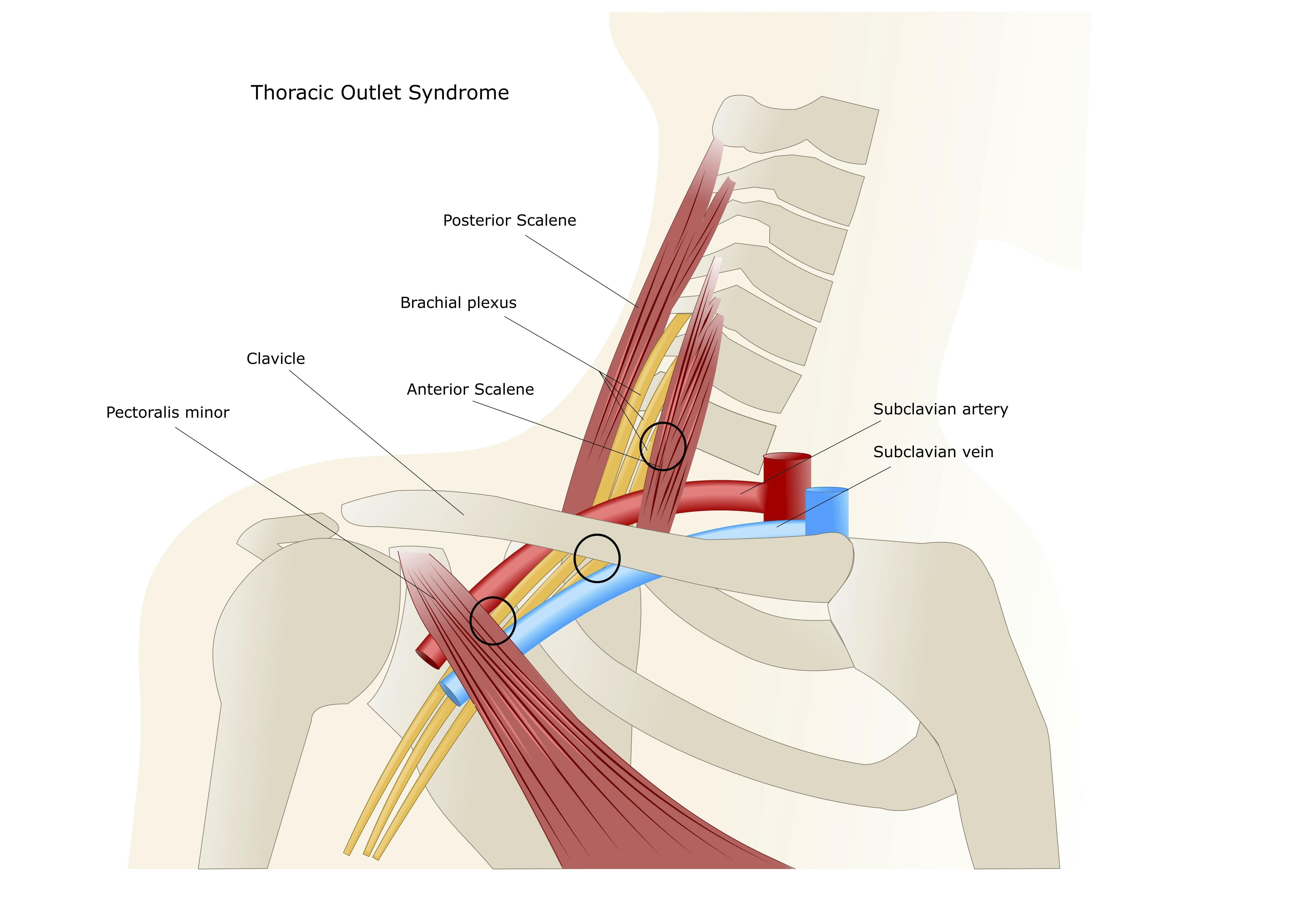
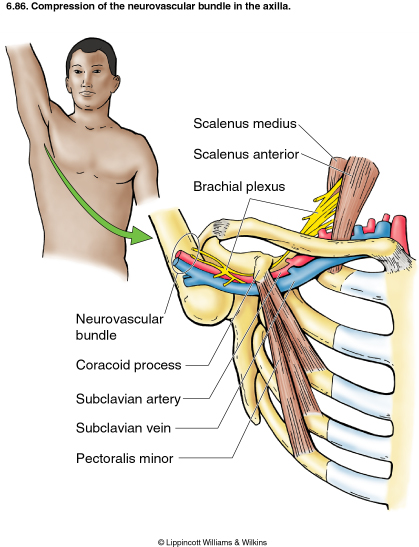
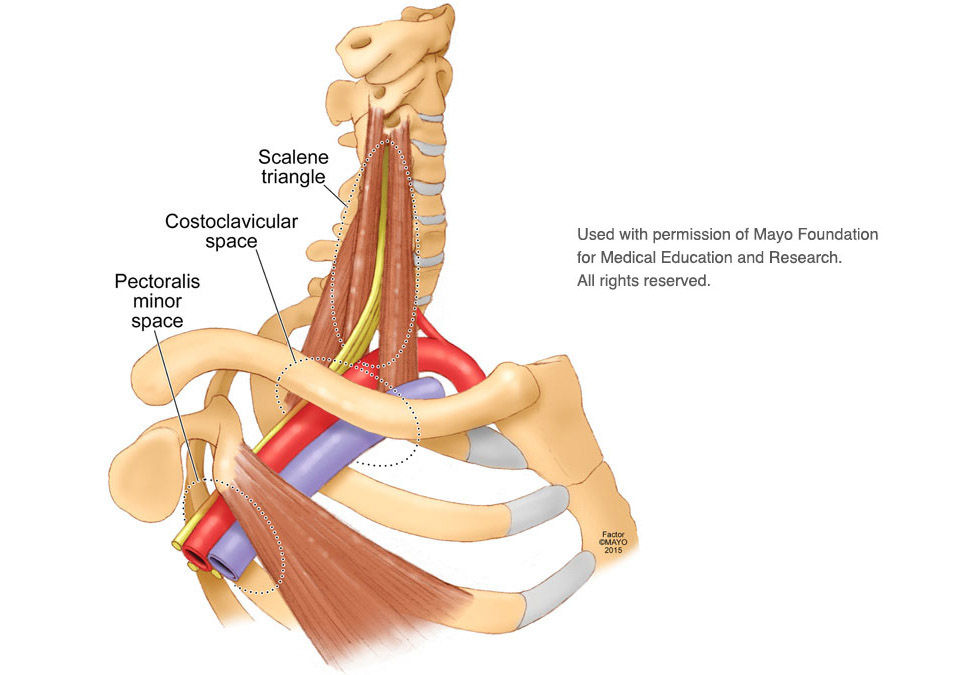
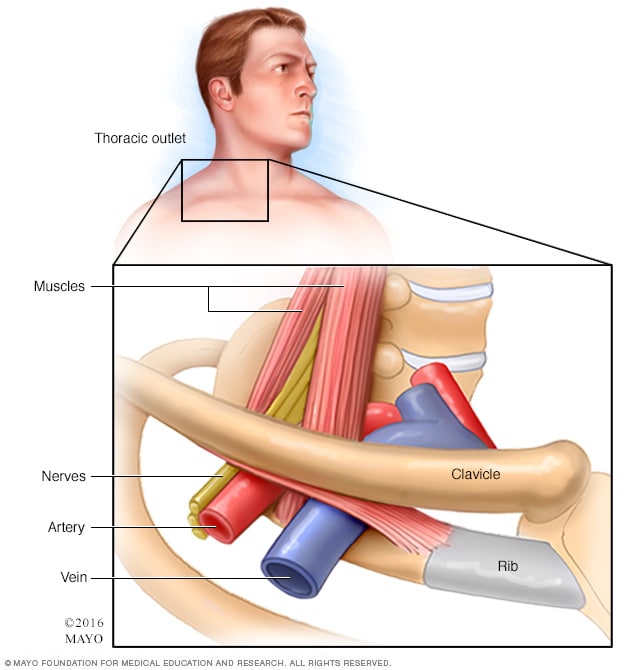
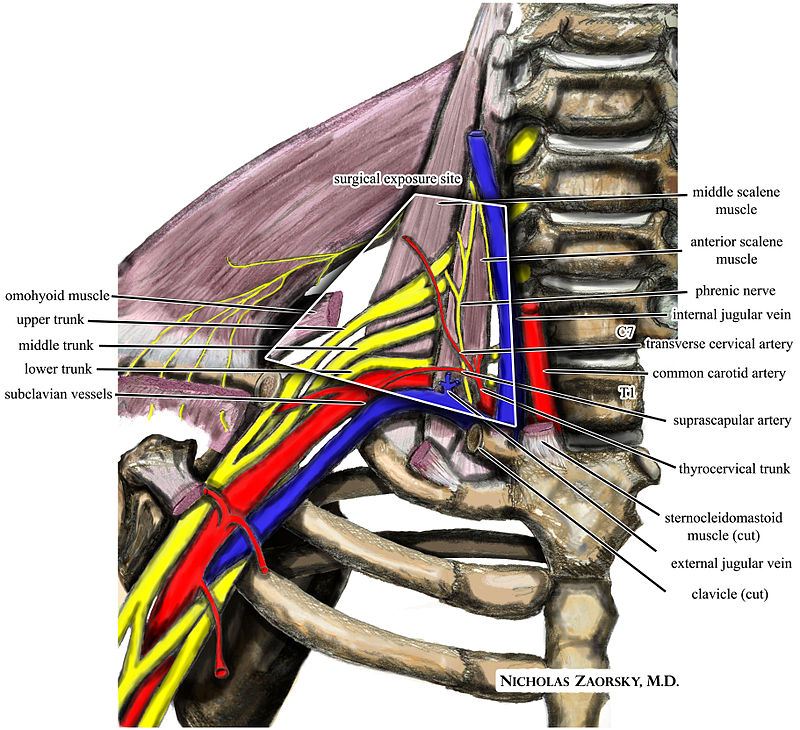
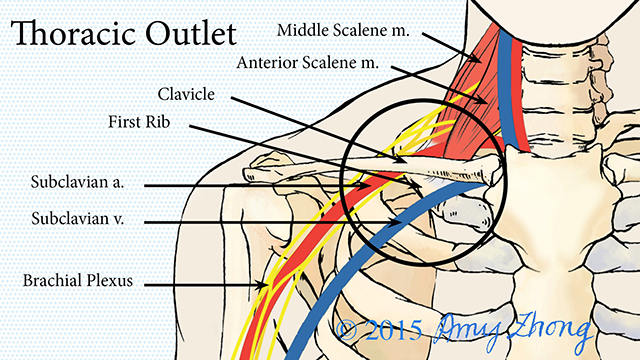
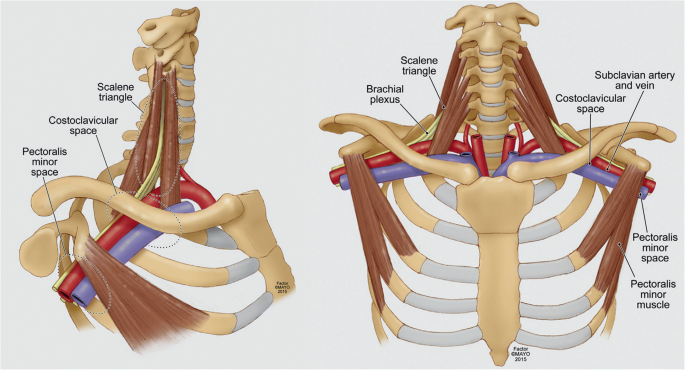
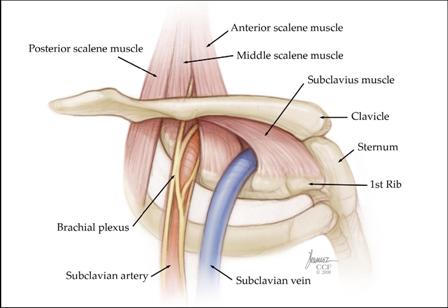
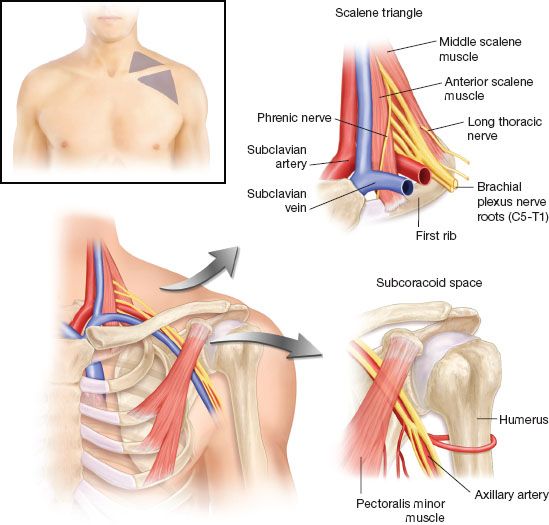
We talk about what health is really like mental health chronic illness disability rare disease cancer and much more. The thoracic outlet is marked by the anterior scalene muscle anteriorly the middle scalene posteriorly and the first rib inferiorly. Most children have normal intelligence but approximately 20 percent of those affected may have intellectual disability delays in reaching developmental milestones andor delays in developing language skills.
The term thoracic outlet syndrome describes compression of the neurovascular structures as they exit through the thoracic outlet cervicothoracobrachial region. X Infantile hypertrophic pyloric stenosis IHPS is a complex disorder with an incidence from 4 to 5 per 1000 live births with a strongly male predilection. Red flags eg cardiac or lung conditions pneumothorax pulmonary embolism peptic ulcers tumours and mesothelioma after exposure to asbestos.
Peer reviewed and up-to-date recommendations written by leading experts. Journal of Vascular Surgery is dedicated to the science and art of vascular surgery and aims to be the premier international journal of medical endovascular and surgical care of vascular diseases.
Scheuermanns syndrome in adolescents.
Providers should consult the Medical Aid Rules and Fee Schedule MARFS for documentation and coding requirements. Annals of Vascular Surgery provides solid peer reviewed coverage of clinical and experimental work in vascular surgery. This disease is the most commonly inherited neurological disorder affecting about one in 2500 people. Published eight times a year Annals includes original research articles basic science research surgical notes and techniques reviews and case reports. Patients with symptoms from compression of the neurovascular bundle in the thoracic outlet are described as having thoracic outlet syndrome TOS which is best thought of as three conditions classified according to which structures are involved. Two forms of Robinow syndrome have been described. The Medical Treatment Guidelines also called Medical Practice Guidelines or Review Criteria are evidence based and were developed by the Office of the Medical Director in. Youll find a community that has your back on The Mighty no matter what health situation youre going through. Neurology articles covering symptoms diagnosis staging treatment prognosis and follow-up.
Currently there are no curative treatments for this disorder with. The term thoracic outlet syndrome describes compression of the neurovascular structures as they exit through the thoracic outlet cervicothoracobrachial region. Most children with Robinow syndrome experience growth delays after birth resulting in slight to moderate short stature. CharcotMarieTooth disease CMT is a hereditary motor and sensory neuropathy of the peripheral nervous system characterized by progressive loss of muscle tissue and touch sensation across various parts of the body. Two forms of Robinow syndrome have been described. Neurogenic thoracic outlet syndrome NTOS is a chronic painful and disabling condition. Most children have normal intelligence but approximately 20 percent of those affected may have intellectual disability delays in reaching developmental milestones andor delays in developing language skills.























:format(jpeg)/cdn.vox-cdn.com/uploads/chorus_image/image/50239787/usa-today-9385250.0.jpg)








Post a Comment for "Thoracic Outlet Syndrome Disability"