Pulmonary Disease Pattern Ecg
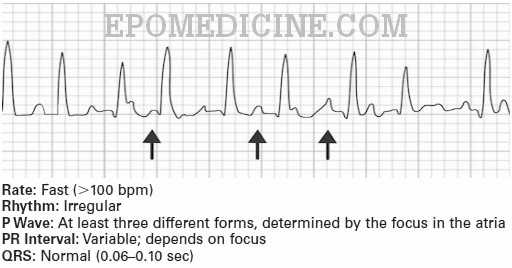
Pulmonary disease pattern ecg. The most common ECG finding in the setting of a pulmonary embolism is sinus tachycardia. In absence of any symptoms your EKG is being interpreted as that of Pulmonary disease leads me to believe that it is compterised interpretation and NOT that of a qualified doctor. There are various deviations from the normal and no consistent pattern with worsening of airway obstruction.
Pulmonary embolism PE poses a challenge to physicians as it can be difficult to diagnose but results in significant mortality and morbidity in patients. I normal pulmonary function pattern 2 restrictive pattern 3 combined obstructive and restrictive pattern 4 obstructive pattern with a residual volume of 100-200 of predicted and 5 ob structive pattern with a residual volume of greater than 200 of predicted. Patients with chronic obstructive pulmonary.
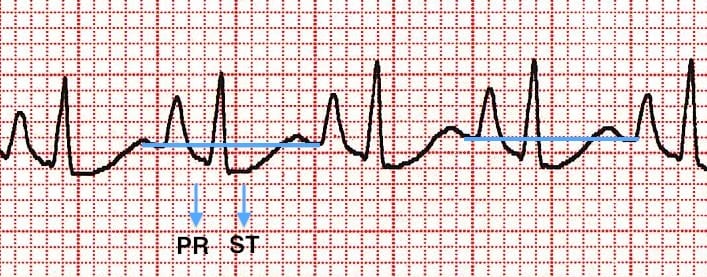
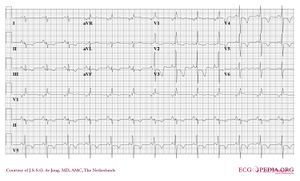
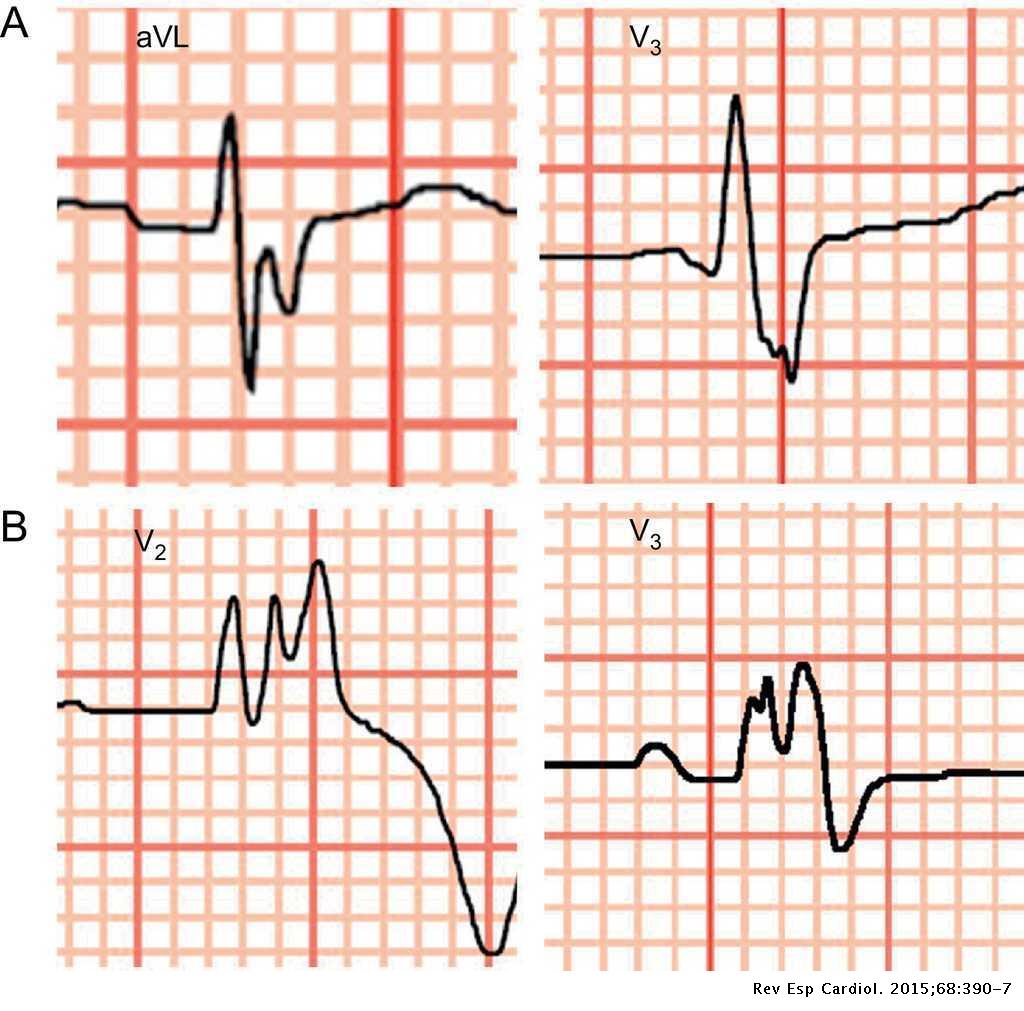
Electrocardiography ECG in Pulmonary Disorders. An R wave 7 mm in V1 or V2. The ECG changes described above are not unique to PE.
Increased pressure in R atria and ventricle Changes in R heart lead to arrhythmia. The ECG may direct you to consider PE under the appropriate clinical scenario In patients with suspected or documented PE the presence of ECG markers suggests hemodynamically significant PE acute cor pulmonale The most important unfavorable prognostic sign is new incomplete or complete RBBB. Diagnosing PE requires an integrated approach using clinical findings electrocardiography ECG blood investigations and imaging modalities.
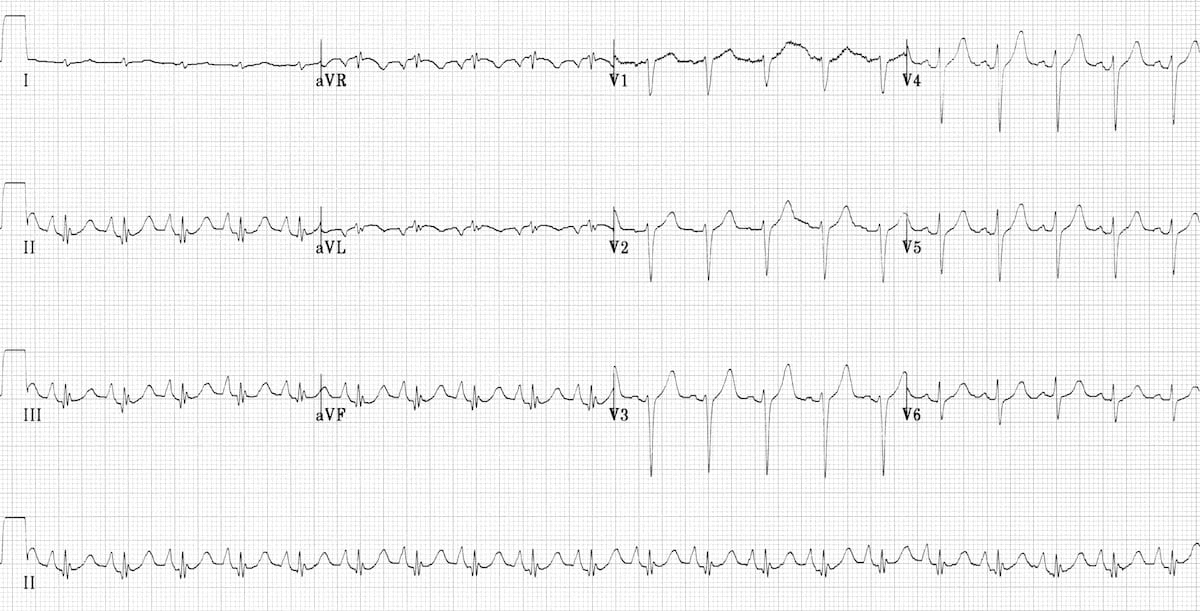
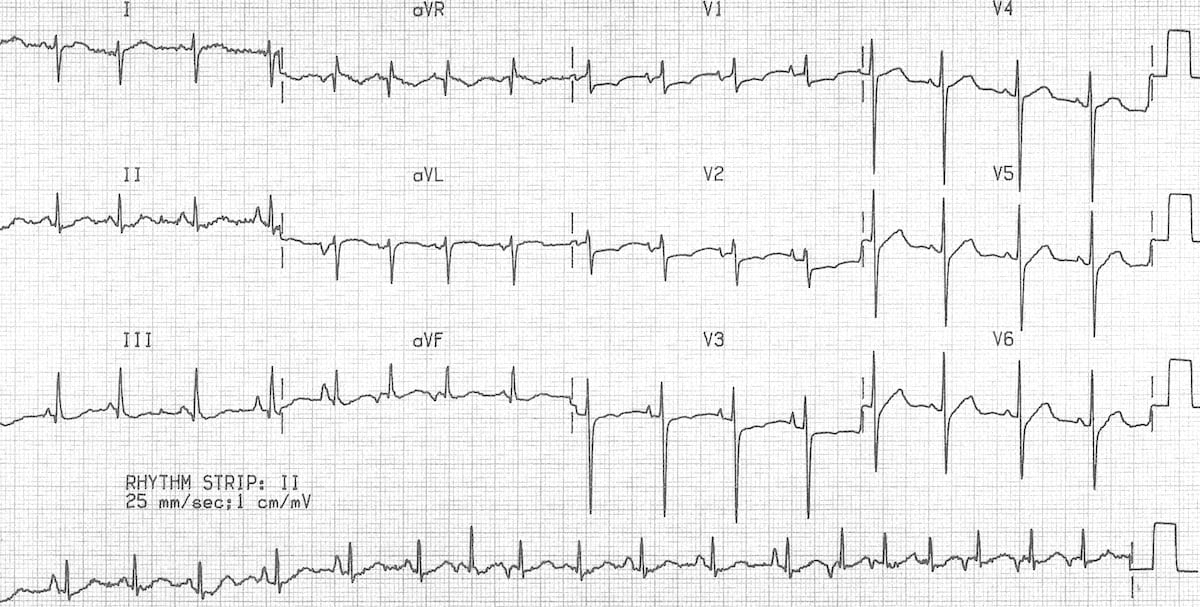
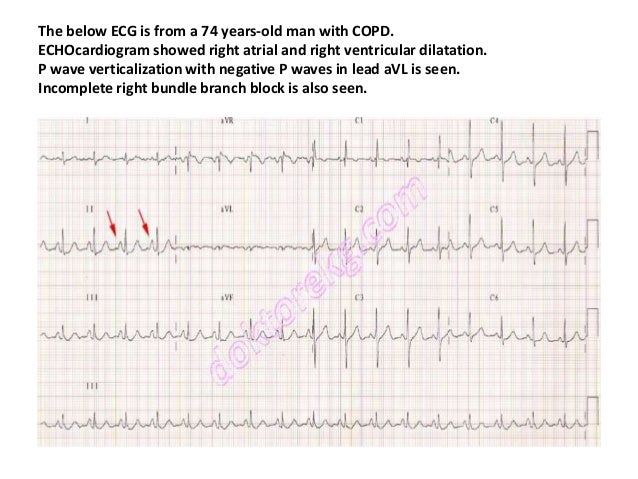
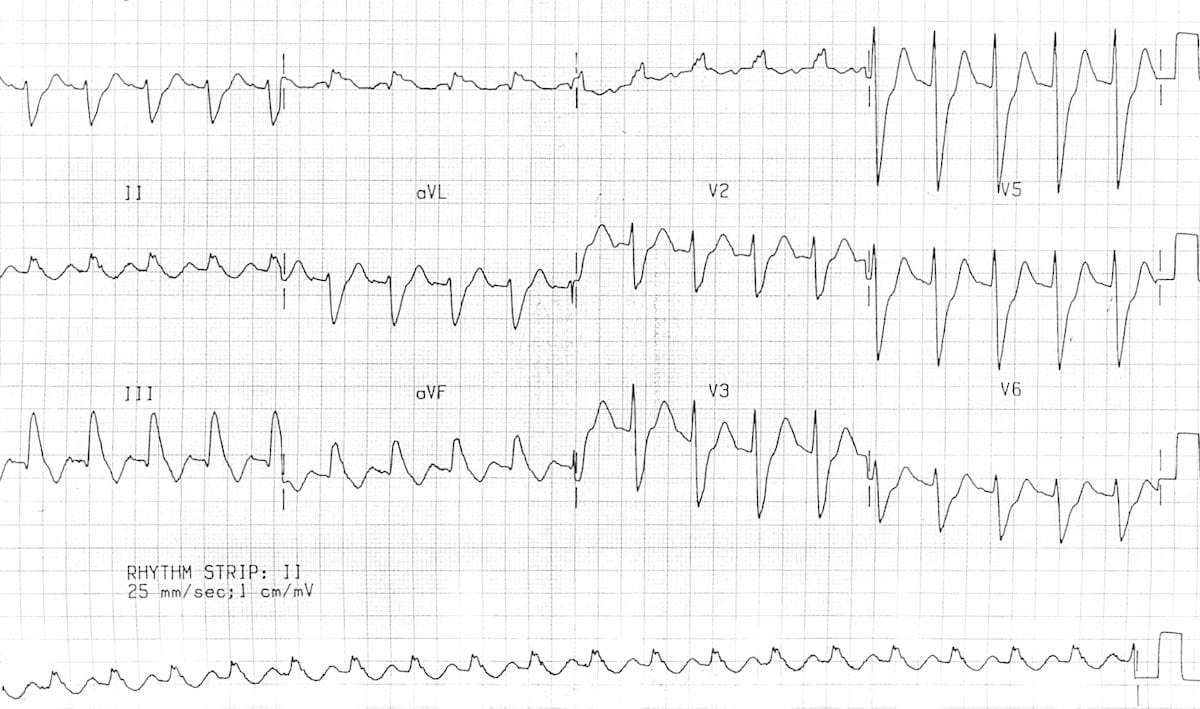
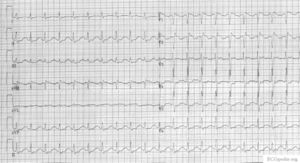
Chronic Pulmonary Disease Pattern An example of right ventricular hypertrophy and right atrial enlargement in a patient with chronic pulmonary hypertension due to peripheral embolisation. Right Ventricular Hypertrophy RVH I. This is termed the.
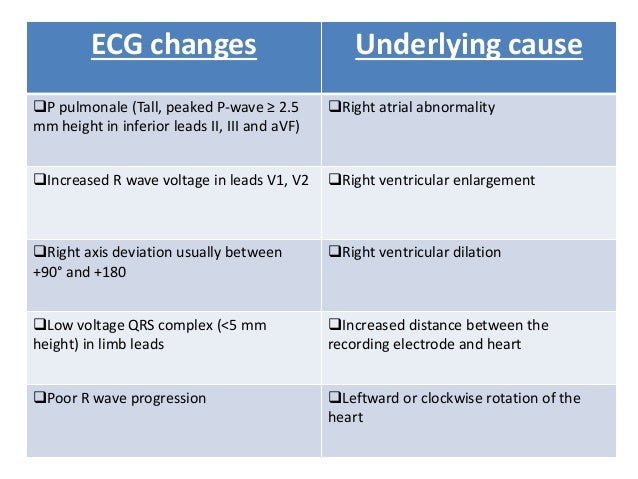
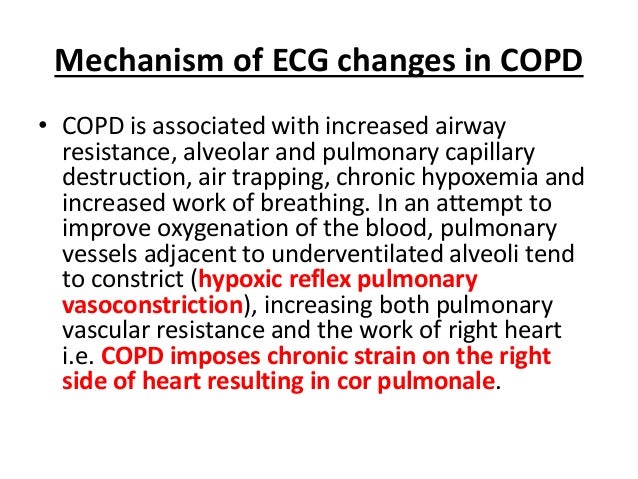
Electrocardiography ECG is a useful adjunct to other pulmonary tests because it provides information about the right side of the heart and therefore pulmonary disorders such as chronic pulmonary hypertension and pulmonary embolism. Any disease that causes right ventricular strain hypertrophy due to hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction. Vessels near hypoventilated alveoli constrict Scarring and arteriosclerosis of the lungs.
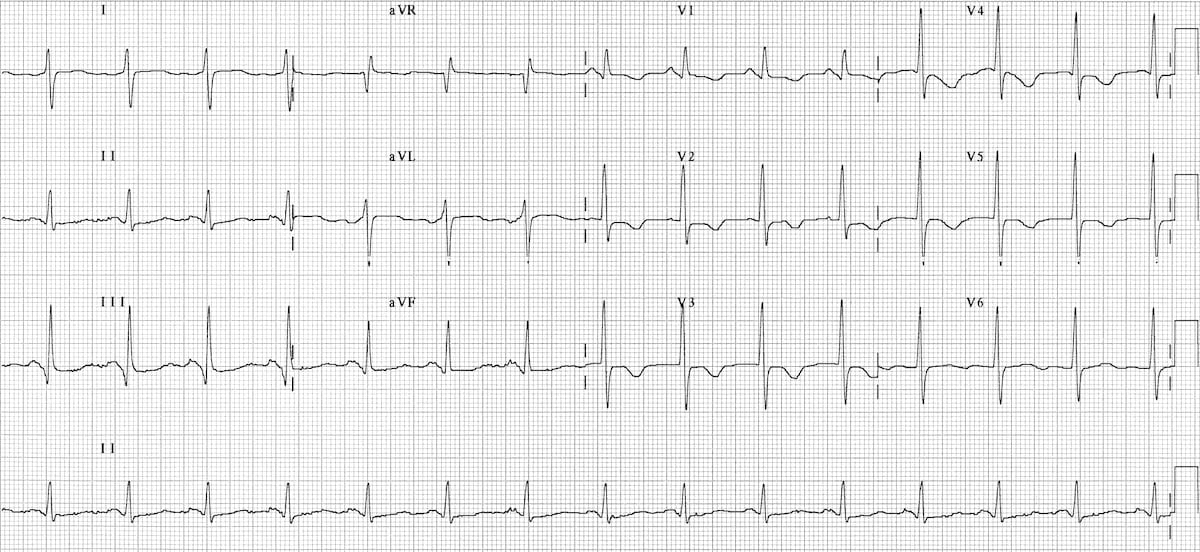
Patients with pulmonary embolism PE can show changes on the ECG. Electrocardiograms were recorded during each pa.
The ECG changes described above are not unique to PE.
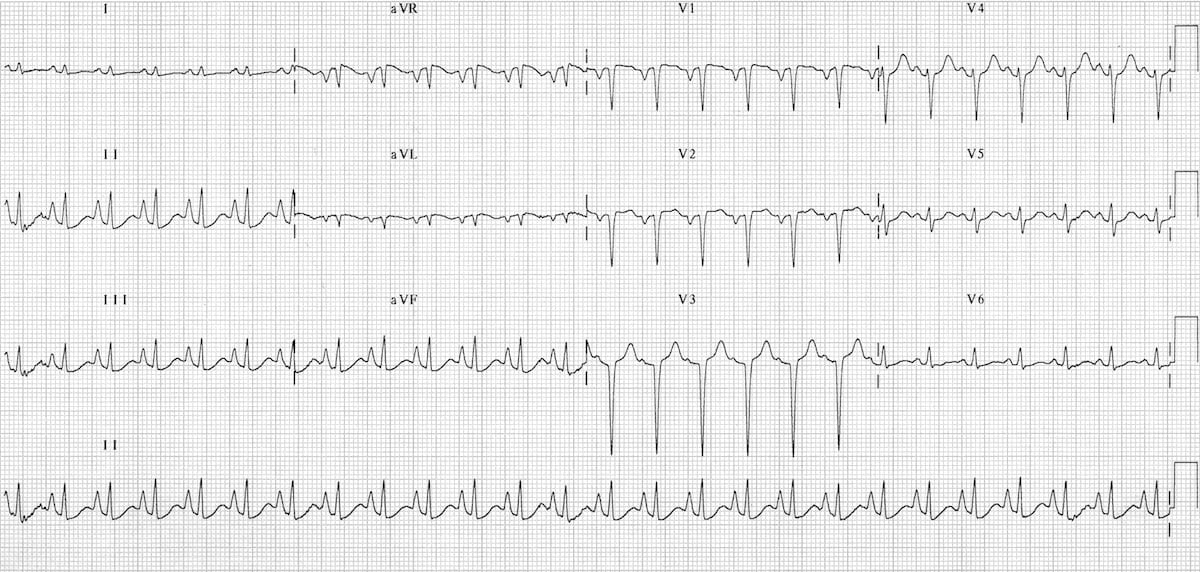
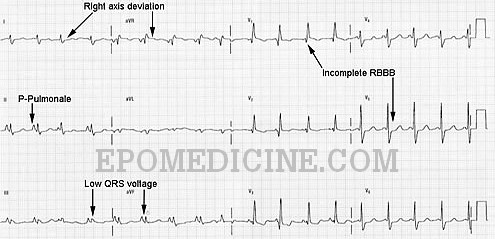
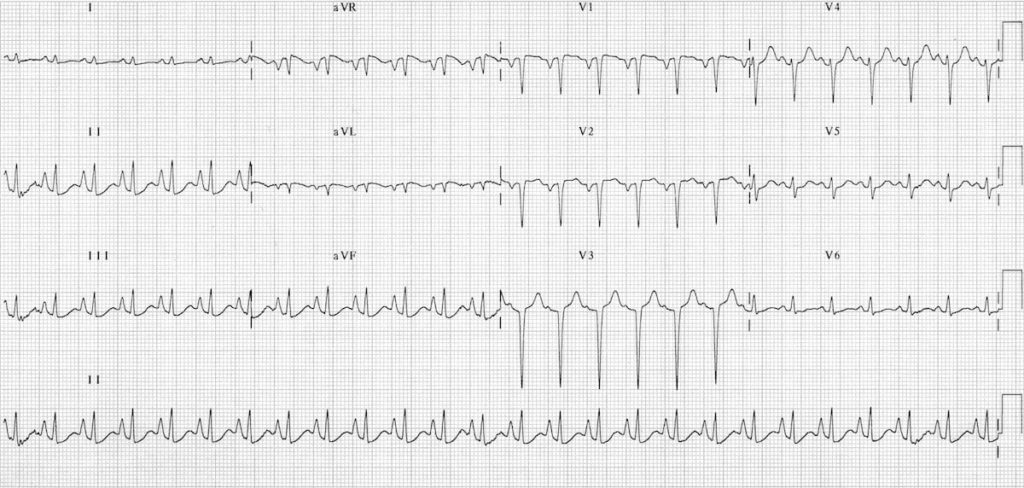
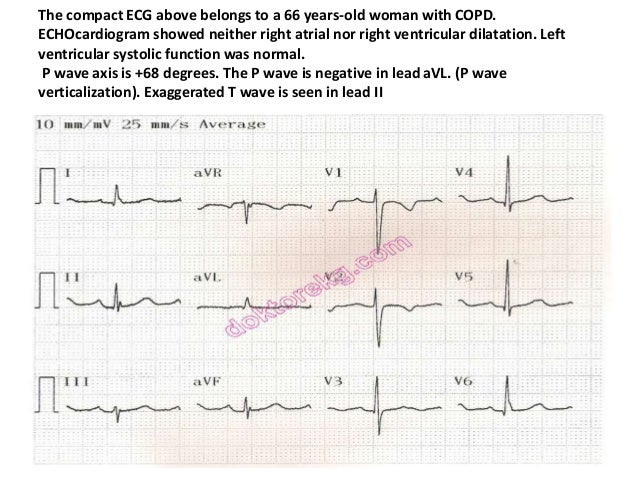
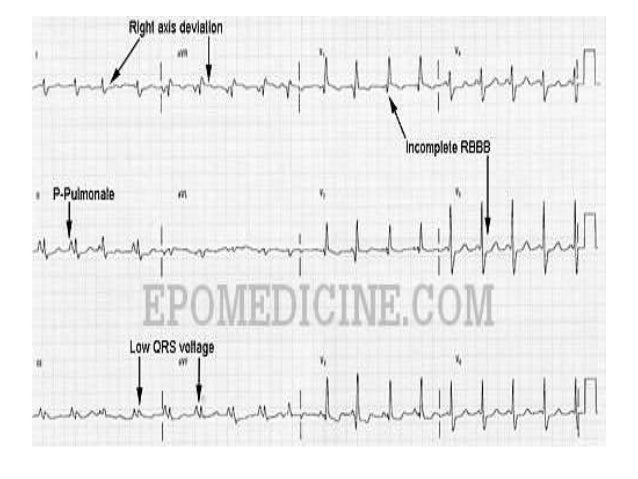
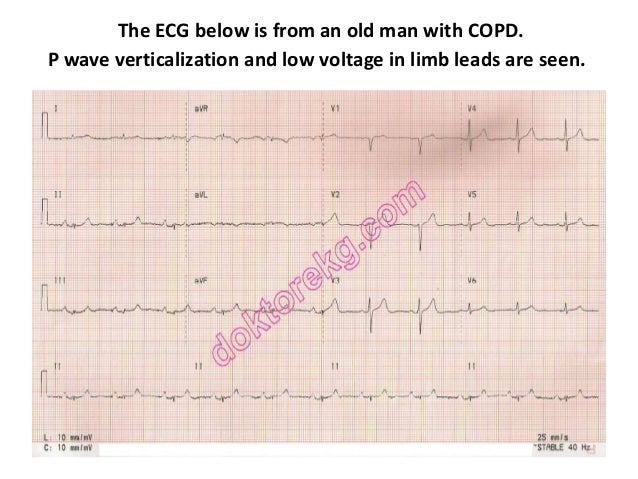
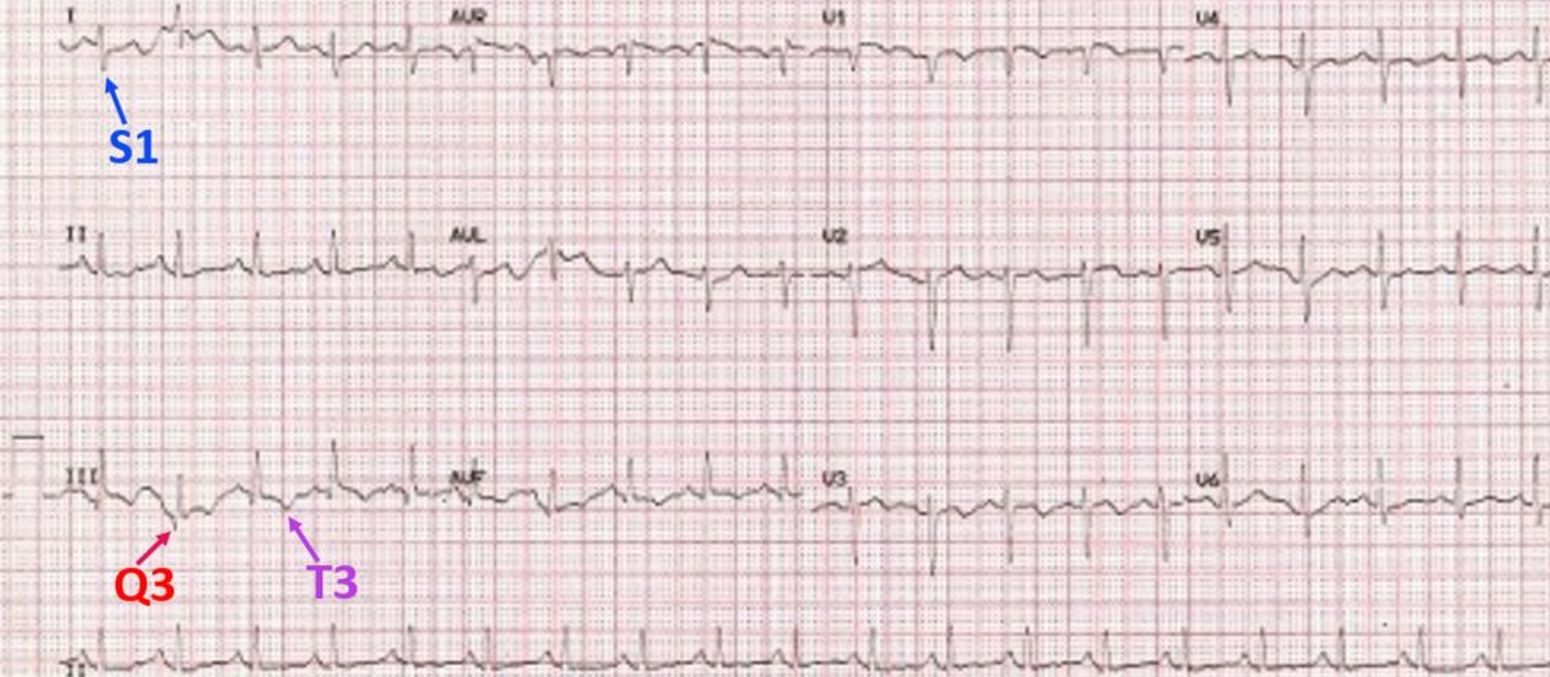
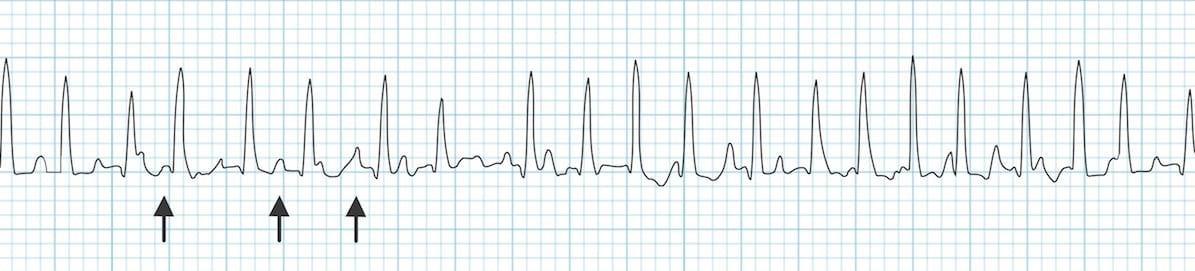
However the S1Q3T3 pattern of acute cor pulmonale is classic. Prominent P waves in the inferior leads right atrial abnormality. The combination of any of the follow ECG changes suggests increased pulmonary and RV pressures knonw as. Or there is some other finding like right atrial enlargement on EKG which you have not copied. There are various deviations from the normal and no consistent pattern with worsening of airway obstruction. Chronic Pulmonary Disease Pattern An example of right ventricular hypertrophy and right atrial enlargement in a patient with chronic pulmonary hypertension due to peripheral embolisation. The ECG shows low voltage QRS complexes in leads I II and III and a right axis deviation. Increased work of breathing Pulmonary hypertension. Any disease that causes right ventricular strain hypertrophy due to hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction.
Chronic Pulmonary Disease Pattern An example of right ventricular hypertrophy and right atrial enlargement in a patient with chronic pulmonary hypertension due to peripheral embolisation. Any disease that causes right ventricular strain hypertrophy due to hypoxic pulmonary vasoconstriction. Pulmonary embolism PE poses a challenge to physicians as it can be difficult to diagnose but results in significant mortality and morbidity in patients. Electrocardiograms were recorded during each pa. Deep S wave in V6 7 mm. Persistent S waves in lead V6. The ECG changes described above are not unique to PE.




















Post a Comment for "Pulmonary Disease Pattern Ecg"