X Linked Dominant Disease
X linked dominant disease. In this disorder there is an excessive accumulation of neutral glycosphingolipids in the vascular endothelium smooth muscle and epithelial cells. X-linked dominant inheritance with lethality in hemizygous males is a rare mode of inheritance. Male and female both are affected.
A number sign is used with this entry because of evidence that X-linked dominant Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease-6 CMTX6 is caused by mutation in the PDK3 gene 300906 on chromosome Xp22. A X-linked monogenic disease that has_material_basis_in dominant inheritance. In males who have only one X chromosome a variant in the only copy of the gene in each cell causes the disorder.
The abnormal gene dominates the gene pair. Cystic fibrosis sickle cell disease. Danon disease is an X-linked dominant disorder characterized by intracytoplasmic vacuoles containing autophagic material and glycogen in cardiac and skeletal muscle cells in patients with cardiomyopathy and skeletal myopathy with or without conduction defect WPW syndrome visual acuity abnormalities due to choriocapillary ocular atrophy or mental retardation 6678.
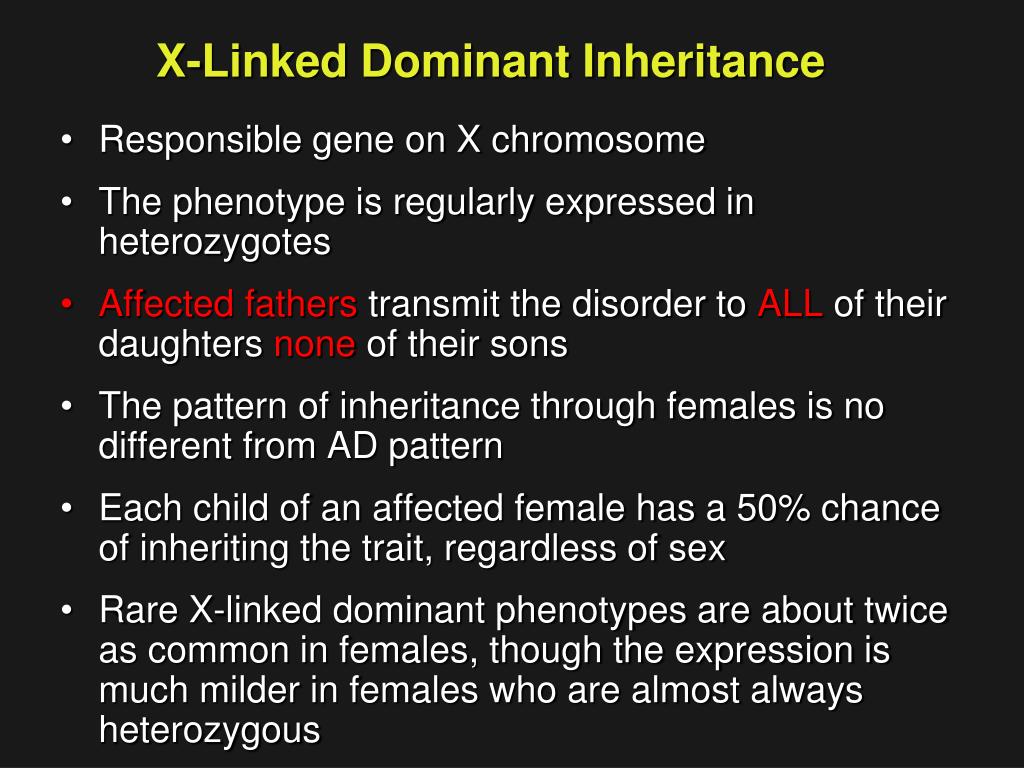
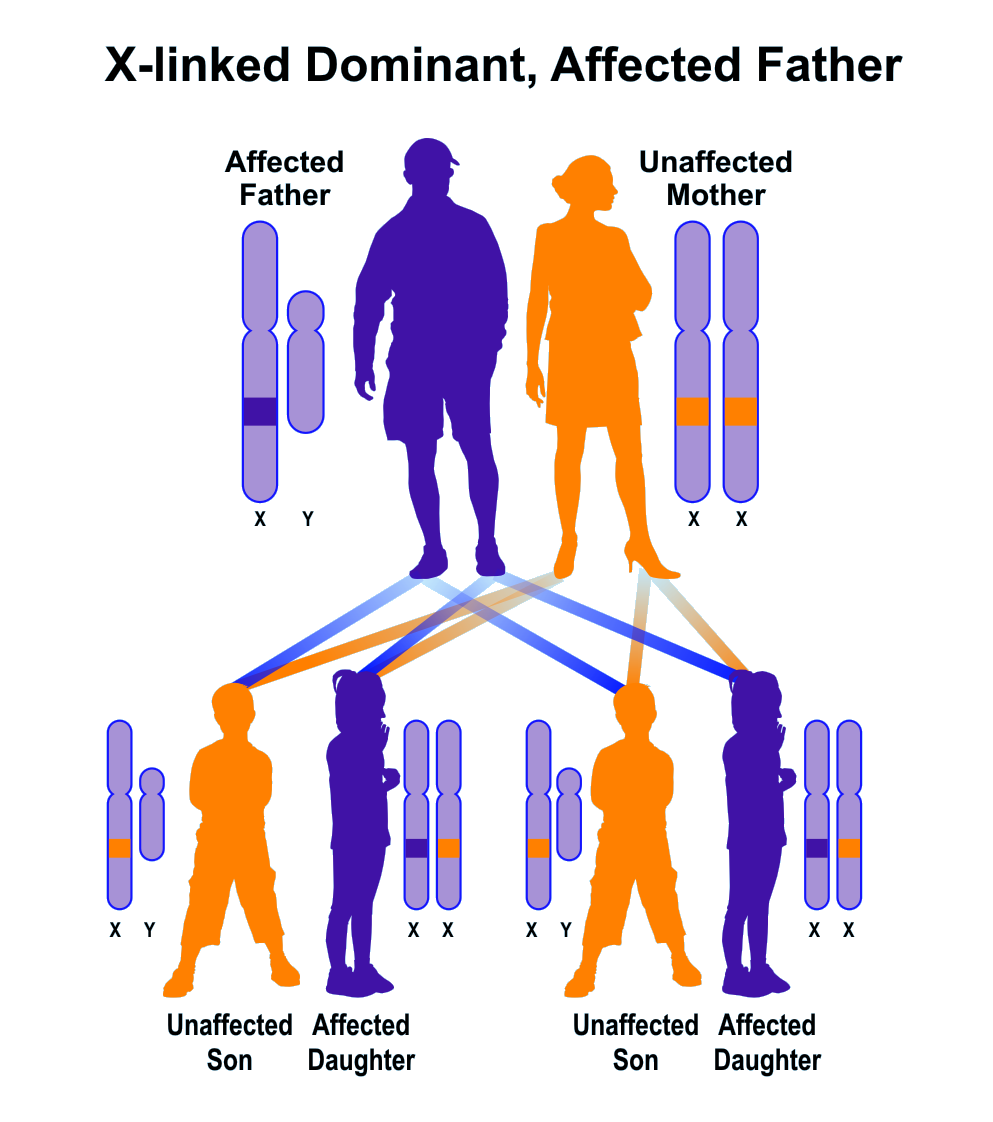
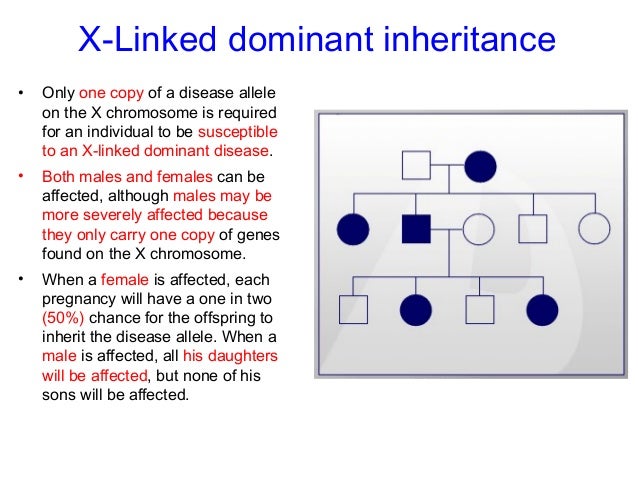
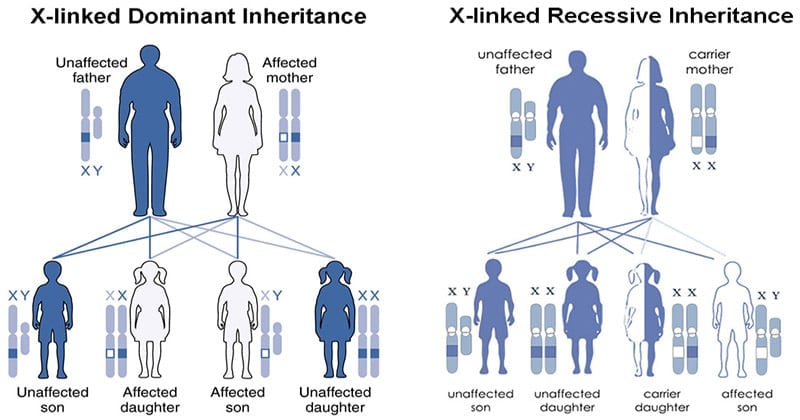
Female carriers are usually mildly affected and have a 50 risk of transmitting the disease to. Summary X Linked Dominant vs X Linked Recessive. It can cause bone deformity including short stature.
In Alport syndrome AS a spectrum of phenotypes ranging from progressive renal disease with extrarenal abnormalities to isolated hematuria with a non-progressive or very slowly progressive course is observed. People with this disease often have progressive loss of the fatty covering myelin that surrounds the nerves in the brain and spinal cordThey may also have a shortage of certain hormones that is caused by damage to the outer layer. The three best-known disorders which seem to be inherited in this way are incontinentia pigmenti IP Bloch-Sulzberger oral-facial-digital I OFD I syndrome and focal.
X-linked hypophosphatemia XLH is an X-linked dominant form of rickets or osteomalacia that differs from most cases of rickets in that vitamin D supplementation does not cure it. A X-linked monogenic disease that has_material_basis_in dominant inheritance. Genetic Inheritance Autosomal Dominant X-linked Recessive Mitochondrial Disease At most gene locuses you have a version from your mom and a version from your dad.
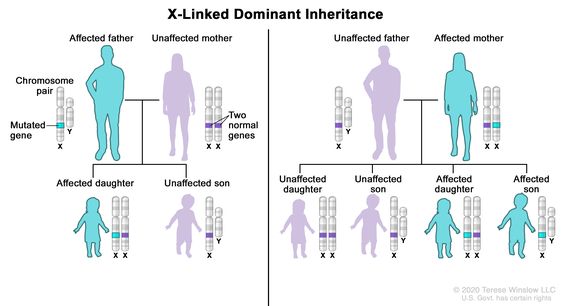
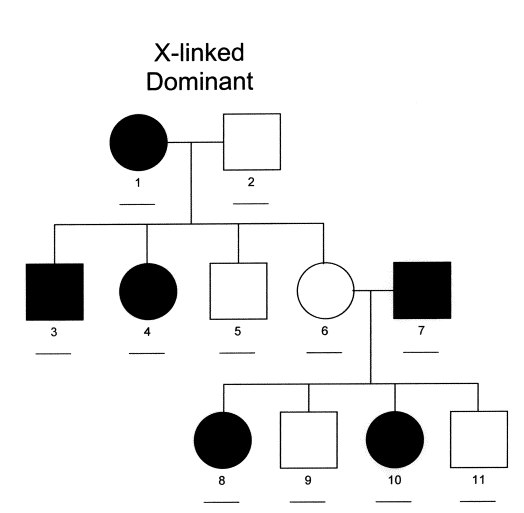
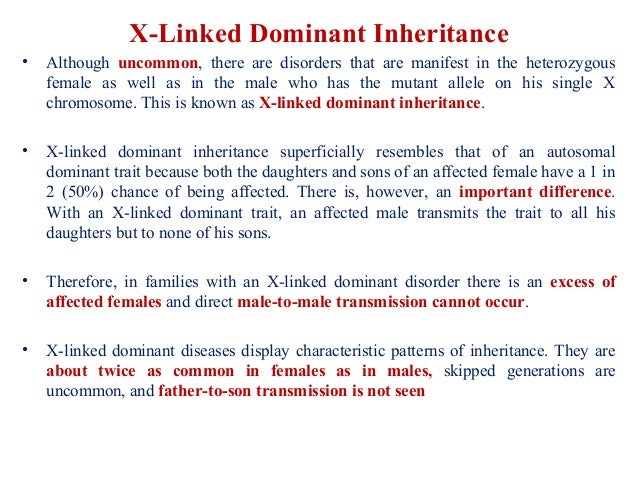
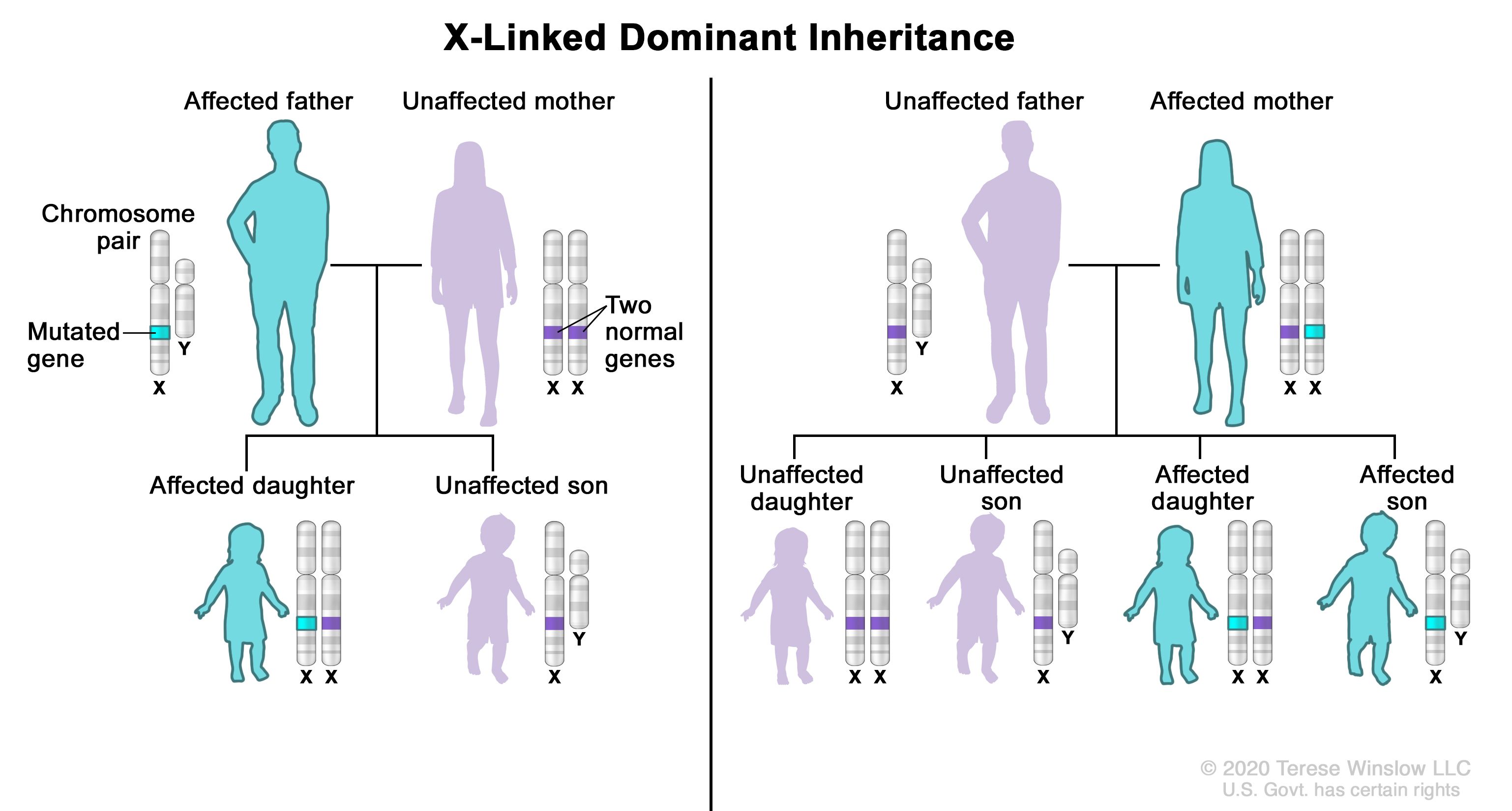
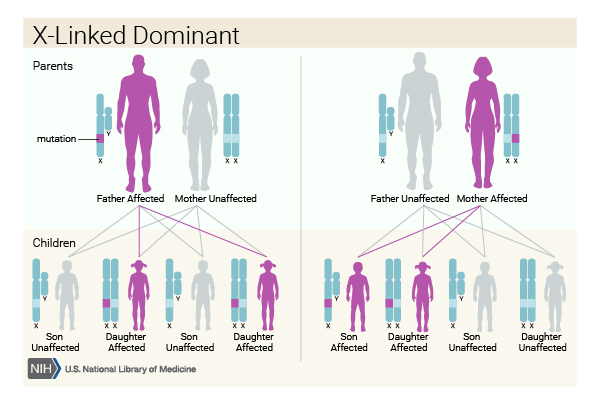
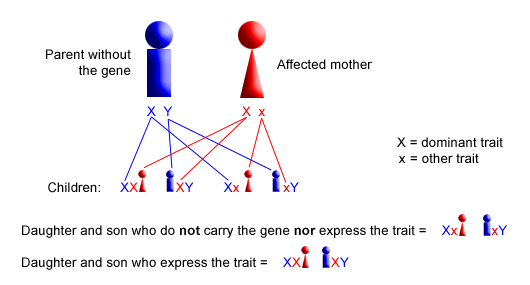
Usually both versions are not expressed and only one of the genes affects the phenotype Observable characteristic. X-linked dominant inheritance sometimes referred to as X-linked dominance is a mode of genetic inheritance by which a dominant gene is carried on the X chromosomeAs an inheritance pattern it is less common than the X-linked recessive type.
Sex-linked diseases are inherited through one of the sex chromosomes which are the X and Y chromosomes.
Female carriers are usually mildly affected and have a 50 risk of transmitting the disease to. Some X-linked dominant diseases. For X-linked dominant diseases however a mutation in one copy of an X-linked gene will result in disease for both males and females. Fabry disease is an X-linked disorder that involves the lysosomes. A number sign is used with this entry because of evidence that X-linked dominant Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease-1 CMTX1 is caused by hemizygous or heterozygous mutation in the GJB1 gene 304040 on chromosome Xq13. X linked dominant and X linked recessive are two conditions. In Alport syndrome AS a spectrum of phenotypes ranging from progressive renal disease with extrarenal abnormalities to isolated hematuria with a non-progressive or very slowly progressive course is observed. X-linked dominant disorders are caused by variants in genes on the X chromosome. In medicine X-linked dominant inheritance indicates that a gene responsible for a genetic disorder is located on the X chromosome and only one copy of.
Approximately 15 is autosomal recessive ARAS and approximately 20 is autosomal dominant ADAS. Female carriers are usually mildly affected and have a 50 risk of transmitting the disease to. Cystic fibrosis sickle cell disease. X linked dominant and X linked recessive are two conditions. Usually both versions are not expressed and only one of the genes affects the phenotype Observable characteristic. Dominant inheritance occurs when an abnormal gene from one parent can cause a disease even though a matching gene from the other parent is normal. X-linked dominant disorders are caused by variants in genes on the X chromosome.




























Post a Comment for "X Linked Dominant Disease"